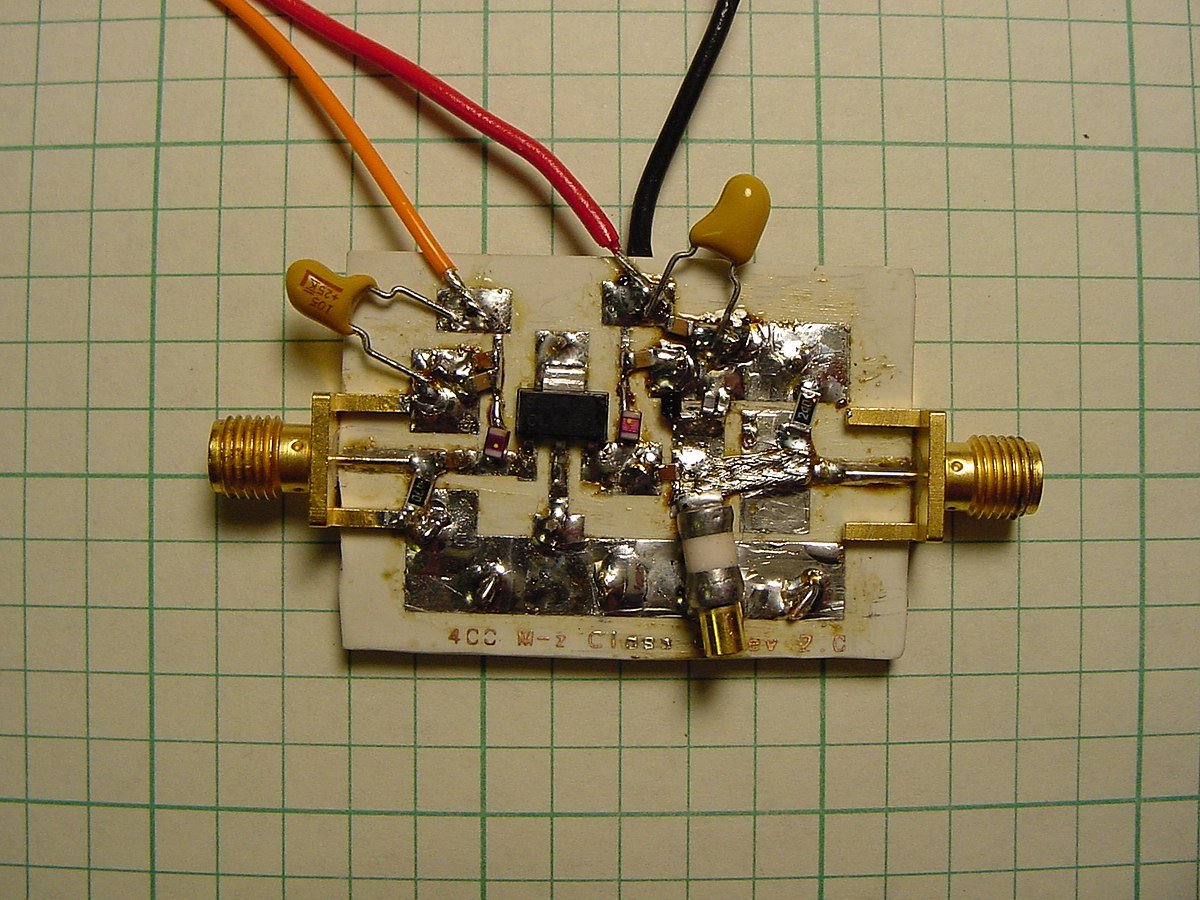
What do you think makes a power amplifier RF an essential component in many radio frequency applications? Understanding how these devices function and their importance in various fields can help you appreciate the technology behind wireless communication, broadcasting, and even hobbyist projects.
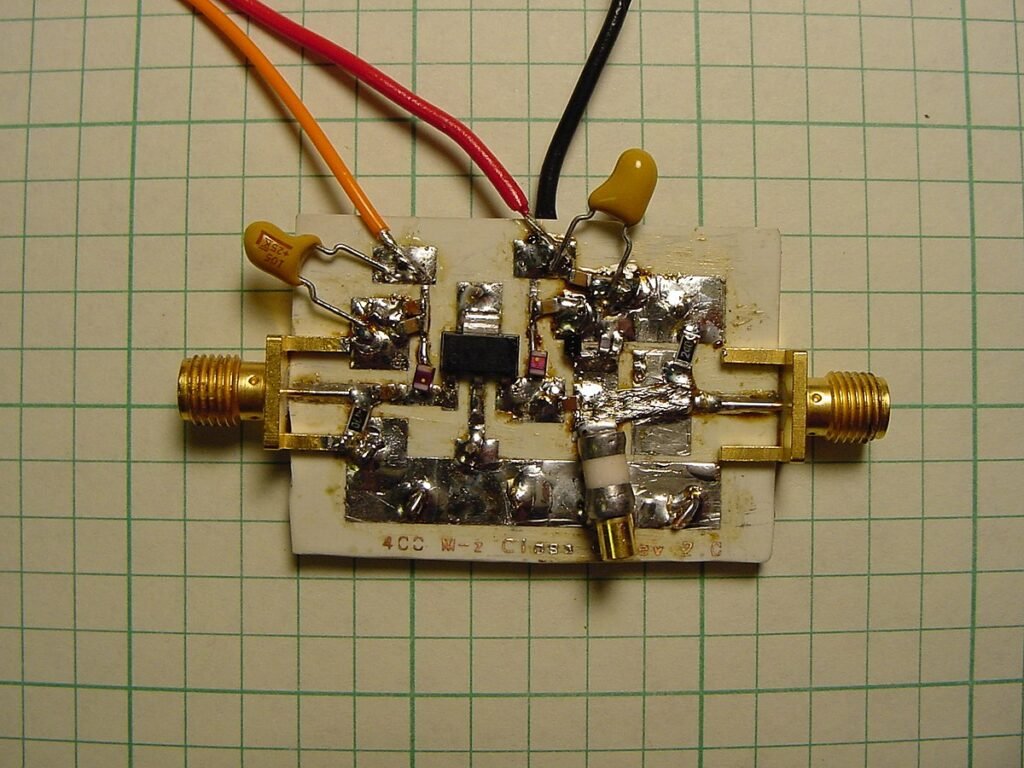
This image is property of upload.wikimedia.org.
What is a Power Amplifier RF?
A power amplifier RF is specifically designed to boost the power level of radio frequency signals. It takes weak electrical signals from sources such as transmitters and strengthens them for transmission over longer distances. This amplification ensures that the signal maintains its integrity and can be received clearly by intended devices.
Power amplifiers play a crucial role in several applications, including cellular communication, broadcasting, and radar systems. By converting low-level signals into powerful outputs, these amplifiers ensure efficient communication and data transfer.
The Role of RF in Power Amplifiers
Understanding Radio Frequency (RF)
Radio frequency refers to the oscillation rate of electromagnetic radiation within the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz. RF is widely used in various technologies, from AM/FM radio and television to wireless communication systems like mobile phones and Wi-Fi.
When you use a device that transmits RF signals, like a smartphone, the RF power amplifier ensures the signal can travel long distances. Without it, the signals would likely dissipate quickly, resulting in poor communication quality.
Why Power Amplifiers Are Important
Imagine trying to hear a whisper in a crowded room. Without proper amplification, that whisper would be lost amidst the noise. Power amplifiers serve a similar purpose in the world of RF, amplifying weak signals so they can be transmitted effectively over longer distances.
Power amplifiers are vital in overcoming losses due to transmission lines, antennas, and other factors that can degrade signal quality. Their ability to increase signal strength directly impacts communication reliability, efficiency, and clarity.
Key Components of an RF Power Amplifier
Input Stage
The input stage receives the weak RF signal and prepares it for amplification. It often includes matching networks that optimize the signal for the subsequent amplification process. Ensuring proper impedance matching in this stage is crucial to maximize power transfer and minimize reflections.
Amplification Stage
The amplification stage is where the magic happens. This section uses transistors or other active components to increase the power level of the input signal. The choice of transistor, such as bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) or field-effect transistors (FETs), affects the amplifier’s performance characteristics, including gain, linearity, and efficiency.
Types of Amplifiers Used
Different types of amplifiers serve distinct purposes:
-
Class A Amplifiers: Known for their high linearity and low distortion, Class A amplifiers are typically used in applications requiring excellent signal quality. However, they tend to have lower efficiency.
-
Class B and Class AB Amplifiers: These are commonly used in RF applications. Class B amplifiers provide a good balance between performance and efficiency, while Class AB amplifiers offer improved linearity at the cost of slightly reduced efficiency.
-
Class C Amplifiers: Primarily used in high-frequency applications, Class C amplifiers offer the highest efficiency. They are well-suited for applications where linearity is less critical, such as in certain types of transmitter circuits.
Output Stage
In the output stage, the amplified signal is delivered to the antenna or transmission medium. This stage often includes additional matching networks to ensure seamless transfer of power from the amplifier to the antenna.
Factors Affecting RF Power Amplifier Performance
Several factors can influence the performance of RF power amplifiers. Understanding these elements can help you choose the right amplifier for your specific application.
Gain
Gain refers to how much the amplifier increases the input signal’s strength. It’s vital to select an amplifier with the appropriate gain to ensure that the output signal meets the necessary power levels for transmission.
Linearity
Linearity indicates how accurately the amplifier reproduces the input signal. A highly linear amplifier maintains signal integrity, making it suitable for applications requiring precise signal representation, such as in audio or certain communication systems.
Efficiency
Efficiency is crucial for minimizing power loss. An efficient power amplifier converts a higher percentage of input power into usable output power, reducing heat generation and the need for extensive cooling systems.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the range of frequencies the amplifier can effectively handle. A broader bandwidth allows the amplifier to accommodate a wider range of signals, making it versatile for various applications.
Thermal Management
As power amplifiers generate heat during operation, effective thermal management prevents overheating and ensures reliable performance. This can include the use of heat sinks, fans, or other cooling mechanisms.

This image is property of www.acquitek.com.
Applications of RF Power Amplifiers
Telecommunications
In telecommunications, RF power amplifiers are indispensable for cellular networks. They boost the signals transmitted between cell towers and mobile devices, ensuring clear voice and data communication.
Broadcasting
For radio and television broadcasting, power amplifiers are essential to deliver strong signals over vast distances. They ensure that broadcasts can reach audiences even miles away from the transmission source.
Radar Systems
RF power amplifiers are also integral to radar systems, which are used for various purposes, including weather monitoring, navigation, and military applications. They enhance the emitted radar signals, improving detection capabilities and range.
Medical Imaging
In medical imaging technologies such as ultrasound, RF power amplifiers play a role in providing the necessary signal strength for imaging equipment. They help improve image clarity and quality.
Wireless Communication Technologies
Wireless communication relies heavily on RF power amplifiers for devices such as Wi-Fi routers, Bluetooth devices, and satellite communication systems. They ensure reliable connections and data transfer across different platforms.
Choosing the Right RF Power Amplifier
When searching for the right RF power amplifier, consider the following factors to ensure you make an informed decision.
Application Requirements
Identify the specific requirements of your application, such as frequency range, power level, and linearity. This understanding will guide you in selecting an amplifier that meets your needs effectively.
Test and Measurement Data
Review the technical specifications and test data provided by manufacturers. Look for performance indicators like gain, efficiency, linearity, and bandwidth, ensuring they align with your application requirements.
Environmental Conditions
Consider the operating environment of the amplifier. High temperatures, humidity, and other environmental factors can affect performance. Select an amplifier that can withstand such conditions if needed.

This image is property of quanticcorry.com.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even the best-designed RF power amplifiers can encounter problems. Knowing how to troubleshoot common issues can save you time and effort.
Overheating
If the amplifier becomes excessively hot, it may be a sign of inadequate cooling, excessive input signal levels, or a faulty component. Ensure proper heat dissipation methods are in place, and check for any damaged components.
Distortion
Distortion in the output signal can indicate improper biasing, insufficient linearity, or operating outside the amplifier’s specified limits. Verify the amplifier is functioning within its intended range and adjust bias settings if needed.
Poor Signal Quality
If you experience poor signal quality, check for impedance mismatches between the amplifier and the antenna. This can result in reflections and signal degradation. Also, inspect the connections to ensure they are secure.
Future Developments in RF Power Amplifiers
As technology continues to advance, the design and efficiency of RF power amplifiers are set to evolve. Here are some trends to watch for:
Integration with Advanced Materials
Developments in materials science may lead to more efficient and durable components. The use of advanced semiconductors, such as Gallium Nitride (GaN), shows promise in improving amplifier efficiency and performance.
Miniaturization
The trend towards smaller, more compact devices means RF power amplifiers will need to shrink in size without sacrificing performance. Innovations in design and materials will facilitate this miniaturization process.
Enhanced Efficiency
Future RF power amplifiers are expected to focus even more on energy efficiency. As concerns around energy consumption increase, optimizing amplifiers for lower power usage while maintaining performance will become a priority.

This image is property of www.aethercomm.com.
Conclusion
Understanding RF power amplifiers and their importance can enhance your appreciation of wireless technology. From telecommunications to broadcasting and beyond, these devices play a crucial role in ensuring effective signal transmission.
When selecting an RF power amplifier, consider the specific needs of your application and stay informed about new trends and developments in the field. With ongoing advances, you’re sure to benefit from innovations that enhance performance and efficiency in the future.